February 10, 2006
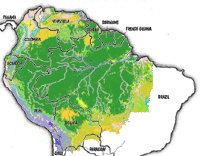
The Amazon River Basin is home to the largest rainforest on Earth. The basin -- roughly the size of the forty-eight contiguous United States -- covers some 40% of the South American continent and includes parts of eight South American countries: Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, and Suriname. Reflecting environmental conditions as well as past human influence, the Amazon is made up of a mosaic of ecosystems and vegetation types including rainforests, seasonal forests, deciduous forests, flooded forests, and savannas. The basin is drained by the Amazon River, the world's largest river in terms of discharge, and the second longest river in the world after the Nile.
World temperatures are higher than in any period over the last 1200 years, according to a study published in the current issue of Science. In reaching their conclusion, a research team from the University of East Anglia in Britain analyzed 14 sets of temperature records including data from rings, fossil shells, ice cores, temperature records, and historical documents from North America, Europe and East Asia.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service today announced that it is considering a petition to list the polar bear as threatened under the Endangered Species Act. Scientists believe polar bear populations are increasingly in danger due to the effects of climate change, specifically receding ice and warming temperatures.
The groundbreaking for the largest solar thermal power plant to be built in 15 years takes place this weekend in Boulder City, Nevada. The 64MW Nevada Solar One power plant will generate enough power to meet the electricity needs of about 40,000 households and follows in the steps of the 354MW solar thermal power plants located in California's Mojave Desert. While California's solar plants have generated billions of kilowatt hours of electricity for the past two decades, the Nevada Solar One plant will use new technologies to capture even more energy from the sun.
Ocean temperatures might have been warmer and sea levels would have risen higher in the 20th century had Krakatoa not erupted in 1883, said a team of scientists. According to the researchers, the release of ashes and aerosols into the upper atmosphere had a significant long-term impact on global climate.
February 9, 2006
While Wal-Mart is a favorite target for a broad spectrum of activist groups, the world's largest retailer has taken a number of steps in recent months to improve the environmental sustainability of its operations: a green Wal-Mart.
Lake Victoria, Africa's largest freshwater lake, is being covertly drained for hydroelectric power according to an article published in the Feb. 11 New Scientist magazine. The report, written by Fred Pearce, says that Uganda is violating a 50-year-old international agreement designed to protect the lake. The following is a release from the New Scientist.
A team of scientists have discovered a new genus and species of dinosaur that is the oldest known and most primitive tyrannosauroid. The newly discovered dinosaur could be described as a mini version of Tyrannosaurus rex.
February 8, 2006
Today South and Central America hold the bulk of the world's remaining tropical rainforests and the region suffers the highest loss of forest of any realm in the world. Most of the forest loss has occurred in the Amazon rainforest where large tracts of land are being cleared for cattle ranches, soybean plantations, and subsistence agriculture. Legal and illegal logging is also widespread in the region. Overall, deforestation rates have increased in South America by almost 17 percent since the end of the 1990s. Rainforest profiles for Latin America:
Belize, Bolivia, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Caribbean islands, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.
Climate change may increase the risk of winter floods and summer water shortages in California says new research by scientists Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The study, which appeared in the January 27 edition of the journal Geophysical Research Letters shows that global warming is likely to change river flows in ways that may result in both increased flood risk and water shortages
February 7, 2006
A team of scientists led by Conservation International (CI) found dozens of new species in a survey of New Guinea's Foja Mountains. The discoveries were made under CI's Rapid Assessment Program (RAP) which deploys expert scientists to poorly understood regions in order to quickly assess the biological diversity of an area. The conservation organization makes RAP results immediately available to local and international decision makers to help support conservation action and biodiversity protection. New Guinea's forests are some of the most biodiverse in the world, but they are increasingly under threat from commercial logging.
A fleet of barges could be used to help protect Europe from plunging into a deep freeze should climate change disrupt Atlantic currents that presently keep the region warm.
February 6, 2006
Since the close of the 1990s, the rate of deforestation in tropical Asia has climbed by more than 20% due to high population growth rates and booming economies. Each year nearly 3 million hectares (11,583 square miles) of forest is permanently cleared while large areas are degraded by logging and wildfires set for agricultural clearing. Lately, much of the large-scale commercial clearing of Asia's tropical forests results from the conversion of natural vegetation to oil palm plantations and industrial logging. Illegal timber harvesting is prevalent across much of the region.
Rainforest profiles for tropical Asian and Pacific countries: Australia,
Bangladesh,
Bhutan,
Brunei,
Cambodia,
China,
India,
Indonesia,
Lao P.D.R.,
Malaysia,
Maldives,
Myanmar (Burma),
Nepal,
Pacific Islands
Philippines,
Papua New Guinea,
Singapore,
Sri Lanka,
Taiwan,
Thailand, and
Vietnam.
February 3, 2006
A pair studies in the Amazon rainforest suggest a link between deforestation and an increased risk of malaria. The first study, conducted in the Peruvian Amazon and published in January's issue of the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, found that malaria epidemics in the region were correlated with deforestation. The later research, released in last week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences indicates that forest clearing around settlements in the Brazilian Amazon increases the short-term risk of malaria by creating areas of standing water in which mosquitoes can lay their eggs.
February 2, 2006
Malaysian scientists are scouring the rainforests of Johor state in search of the legendary ape-man Bigfoot, supposedly sighted late last year. But they are more likely to encounter some less fantastic but unique creatures that dwell in these still unexplored, but fast-disappearing ecosystems. While most experts agree that the likelihood is remote of finding the "Bigfoot" creature Malaysian tribal people call siamang, mawas, or hantu jarang gigi, the chances of finding such a beast is diminishing rapidly.
Late last week, countries that export and export tropical timber reached a 10-year agreement to help promote the sustainable development of forests while fighting illegal logging. The pact calls on signatories to support and develop tropical timber reforestation projects and share information on forestry management, while promoting the expansion and diversification of international trade in tropical timber from sustainably managed and legally harvested forests. The agreement, which was signed by 33 producing and 26 consuming countries, also aims to improve forest law enforcement and governance, specifically addressing illegal logging which is quite prevalent and extremely costly for developing countries.
February 1, 2006
I updated forestry figures and other statistics for all countries in the world. This has been quite an effort but now the most up-to-date deforestation and forest cover figures are available along with other information. I am about half way through environmental profiles for individual countries--probably another week before these are ready. For now Africa is mostly updated:
Angola,
Benin,
Burkina Faso,
Burundi,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Comoros,
Congo,
DR Congo,
Cote d' Ivoire,
Equatorial Guinea,
Ethiopia,
Gabon,
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Kenya,
Liberia,
Madagascar,
Malawi,
Mauritania,
Mauritius,
Mozambique,
Niger,
Nigeria,
Rwanda,
Senegal,
Sao Tome and Principe,
Seychelles,
Sierra Leone,
Somalia,
Sudan,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda,
Zambia, and
Zimbabwe.
Australia's Great Barrier Reef may be at risk of one of its worst coral bleaching events on record warned a leading Australian scientist Tuesday. Ove Hoegh-Guldberg of the University of Queensland told the Australian Broadcasting Corp. that current temperatures suggest that this year's bleaching event could rival that of 2001-2002, which affected 60 percent of the reef.